If you’re planning to comply with ISO 9001, you probably do not know how the standard is structured and what it requires to implement a QMS. Read further to learn more.
What is the structure of ISO 9001?The ISO 9001 requirements provide a set of standard elements that will guide you in the implementation, maintenance, and improvement of a Quality Management System (QMS). The requirements are designed to be applicable to any kind of organization, for profit or nonprofit, manufacturing or service-based, large or small, regardless of the economic sector. The requirements of ISO 9001 describe which elements are mandatory in a QMS, but not how to implement those necessary elements. Organizations that meet the criteria for ISO 9001 certification (that is, their QMS meets ISO 9001 certification requirements) can achieve ISO 9001 certification, which is often required by important customers.
For more information on ISO 9001 mandatory and non-mandatory documents, see this article: ISO 9001 Documentation Requirements – The complete list.
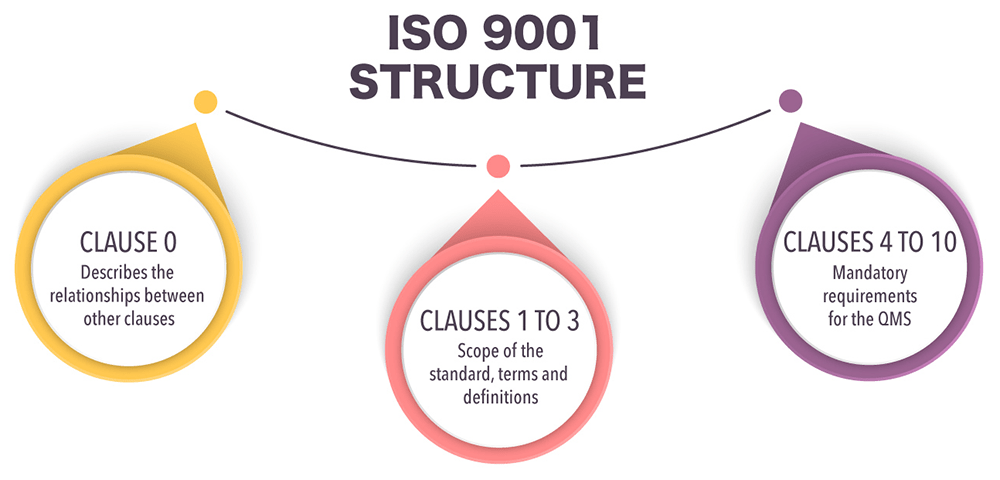
The ISO 9001:2015 requirements are broadly separated into 11 clauses (which are simply ISO 9001 sections).
Clauses 0 to 3 are not mandatory for implementation, while clauses 4 to 10 are mandatory; the exception to this mandatory rule in ISO 9001:2015 is clause 8, from which requirements can be excluded during implementation if the company finds those processes to not be applicable.

Clause 0 mentions the benefits of implementing a QMS and the quality management principles, and it presents the process approach, the Plan-Do-Check-Act cycle, and risk-based thinking. These ISO 9001 elements are important for understanding the sections that follow. People often overlook this clause, but they shouldn’t, as it frames much of the information that comes next, especially about how the various clauses relate to each other.
Clauses 1 through 3 include no requirements, but instead deal with the scope of the standard, references to better understand the standard, and terms and definitions. The remaining clauses include the ISO 9001 requirements for a QMS.
Clause 4 is the first clause of ISO 9001 that contains the ISO 9001 Quality Management System requirements. An organization is not a closed system, isolated from the outside; it is inserted in a particular context and cannot be independent of what customers are looking for, or what regulators define. So, this section deals with the internal and external issues that can influence an organization in setting and meeting its objectives, as well as the interested parties that interact with the QMS. It also includes the requirements about the scope of the QMS and the process mapping and characterization.
The section on leadership outlines the requirements concerning top management, which are:
This section presents the requirements for determining and working with risks and opportunities, as well as those for setting quality objectives, aligned with the Quality Policy, and plans to meet them.
Clause 7 is a very diverse section that includes requirements for management to provide resources, i.e., human resources, infrastructure (including equipment, hardware and software, and building facilities), work environment (including temperature control, humidity control, dust control, and sterilization control), the control of any equipment used to monitor or measure the product or service, and the organizational knowledge required to operate the QMS. The importance of competence, awareness, and communication for human resources is emphasized.
Of all the ISO 9001 2015 clauses, this section is the only part of the standard where a company can choose to exclude sections of the requirements (such as excluding the design requirements if your company does not do design work). The requirements deal with planning for product (or service) and include determining and reviewing the product requirements, design and development, and purchasing, followed by manufacturing of a product or provision of a service and its supply. The final requirements deal with quality control and product or service nonconformities.
The performance evaluation section outlines requirements for assessing customer satisfaction, internal audit, monitoring, analysis, and evaluation of process performance. Also included are the requirements of the management review, including the mandatory inputs and outputs for the review.
The last section deals with improving your QMS through corrective actions and continual improvement. This is the final clause of the standard and the completion of the ISO 9001:2015 requirements.
There is also an appendix that clarifies and explains the ISO 9001 principles, as well as the requirements in the preceding clauses, but it does not include further ISO 9001 Quality Management System requirements.
The greatest difficulty when implementing the ISO 9001:2015 requirements is to ensure that the resulting collection of policies, procedures, processes, and records meets the needs of the company and its customers, while still allowing for improvement of the system. Improvement of the system is one of the main reasons for implementing a QMS, as it benefits the company in the long run. A QMS is a system, and a system is more than just the simple sum of answers to requirements.
To implement ISO 9001 requirements yourself, easily and efficiently, get this: ISO 9001 Documentation Toolkit.